surfactant for premature babies side effects
These medications are injected at least 24 hours before the babys birth but ideally no more than a week in advance. RDS typically gets worse over the first 2 to 3 days.

Significant Increase In Premature Babies Surviving Without Disability
Extra care should be taken when giving surfactant to extreme low birth weight infants because this is a population at higher risk for side effects such as severe episodes of airway obstruction during the procedure.

. It can cause babies to need extra oxygen and help with breathing. Artificial surfactant ALEC given to very premature babies at birth significantly reduces their mortality and the respiratory support needed and should prove a. Managing side effects general information.
Data on bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD is often based upon the following classification of preterm infants categorized by BW or GA. Respiratory failure secondary to surfactant deficiency is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Betamethasone or dexamethasone are the two steroids most commonly used in cases of preterm delivery.
Feeding or bowel problems. RDS occurs most often in babies born before the 28th week of pregnancy and can be a problem for babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Less invasive surfactant administration LISA aims to provide an.
BPD can cause swelling and scarring in the lungs. Artificial surfactant had no effect on the incidence of pneumothoraces pulmonary interstitial emphysema patent ductus arteriosus or postnatal infections and no serious side effects. Pale skin slow heartbeat breathing that stops apnea urinating less than usual or.
The health care team will monitor your baby for signs of needing more surfactant. Tell your childs caregivers at once if the child has any of these serious side effects. Bleeding around the endotracheal tube.
Immature lungs in premature babies often lack surfactant. Type of surfactant and mode of administration seem to play an important role. However more recently noninvasive methods like least invasive surfactant therapy.
Babies born prior to the completion of their gestation period are highly prone to suffer from hyaline membrane disease. Now both lung surfactants and antenatal corticosteroids are rarely associated with side effects. Your baby will remain under constant supervision during treatment with this medicine.
These effects may result from direct pulmonary or hemodynamic changes or a combination of both but may also be due to rapid alterations of blood gases. Tell your childs doctor if the child has serious side effects of Survanta including. Pulmonary surfactant and.
Prophylactic or very early surfactant administration in very. Surfactant therapy substantially reduces mortality and respiratory morbidity for this population. Blood gases show your babys breathing is more effective Sometimes more than one dose of surfactant is needed.
Does surfactant have any side effects. This is a lung disease that can develop in premature babies as well as babies who have treatment with a breathing machine. The therapy is now considered routine care for women at risk of preterm delivery between 23 and 34 weeks gestationand may.
This is a health condition that affects the airways and can cause breathing problems. Any premature newborn baby having symptoms like difficulty in breathing which may worsen with time tachypnea flaring of the nostrils chest retractions grunting sounds while breathing and cyanosis are suspected to suffer from hyaline. Selective surfactant and continued mechanical ventilation for preterm infants with or at risk for respiratory distress syndrome.
Common side effects of Survanta include. Noisy breathing feeding or bowel problems or. A rare complication of surfactant treatment is pulmonary haemorrhage1 23.
Less serious side effects include. As for any protocol each neonatal intensive care unit should develop a coherent administration strategy with the goal of achieving targeted delivery of surfactant that. This problem can be treated in the neonatal.
Secondary surfactant deficiency also contributes to acute respiratory morbidity in late-preterm and term neonates with meconium. Early surfactant administration with brief ventilation vs. Breathing problems in premature babies are caused by an immature respiratory system.
Preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome RDS requiring surfactant therapy have been traditionally receiving surfactant by intubation surfactant and extubation technique InSurE which comprises of tracheal intubation surfactant administration and extubation. Foam from cow lungs can be transformed into a lifesaving treatment for premature infants struggling to breathe. Transient bradycardia hypotension endotracheal tube blockage decreased oxygen saturation.
Surfactant replacement can increase the chance that the ductus arteriosus remains open. Blood in the urine. Urinating less than usual.
However during administration of lung surfactants transient bradycardia and oxygen desaturation may be observed. The baby is a twin or other multiple multiple birth babies are often premature The mother has diabetes a baby with too much insulin in their body can delay making surfactant The baby has a condition called patent ductus arteriosus PDA. This results in stiff collapsible lungs and increased fluid in the lungs making it hard work to breathe.
Respiratory distress syndrome RDS is a common problem in premature babies. Surfactant replacement therapy for respiratory distress syndrome RDS in preterm infants is a major breakthrough in neonatal medicine. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia also called BPD.
Premature infants may be born before their lungs make enough surfactant. Results from the pertinent literature are summarised with a special emphasis on how to avoid potentially harmful side effects of. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome RDS RDS formerly known as hyaline membrane disease is the major cause of respiratory distress in preterm infants.
Non-invasive ventilation and especially the application of continuous positive airway pressure CPAP has become standard for the treatment of premature infants with respiratory problems. Blood in the urine. It is caused by deficiency of surfactant the.
The open study of infants at high risk of or with respiratory insufficiency the role of surfactant OSIRIS demonstrated that the combined incidence of death or BPD was reduced by about 11 when surfactant was given at a mean postnatal age of 2 h rather than 3 h RR089 95 CI 079 to 100 evidence level 1b showing that even fairly short delays in therapy worsen outcomes. In very low birth weight premature infants surfactant administration may cause pulmonary hemorrhage. Side effects include.
It is likely to be a consequence of increased shunting through a patent ductus arteriosus PDA and. However CPAP failure may occur due to respiratory distress syndrome that is surfactant deficiency. The risk is tiny compared to the benefits of surfactant treatment.
The baby has trouble maintaining body temperature cold stress Infection. Business of turning an animal into a side of beef. Low amounts of surfactant lead to poor lung function.
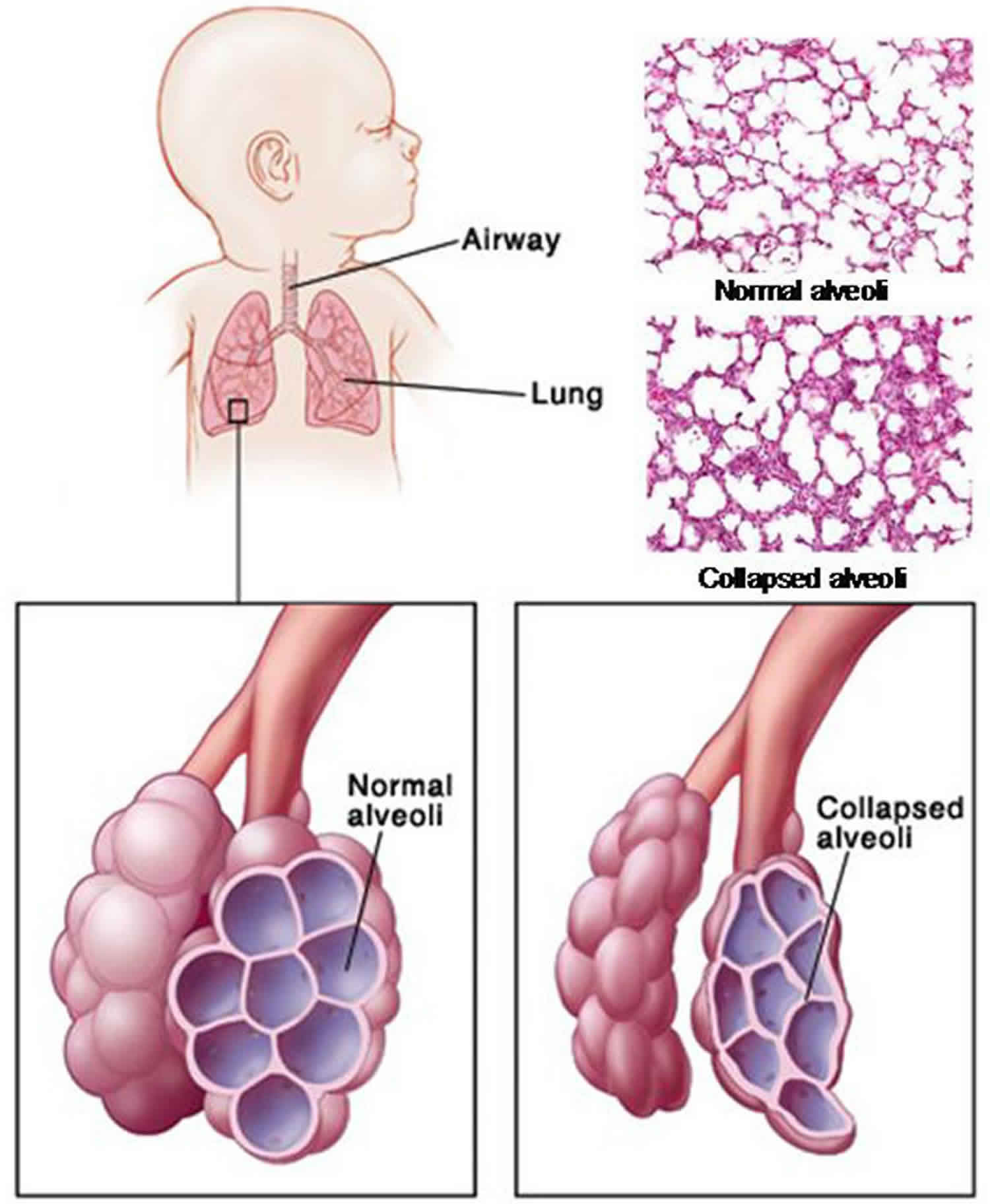
Infant Respiratory Distress Syndrome Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Postnatal Steroids In Premature Babies Where Are We Now Paediatricfoam

Lung Surfactants Nursing Pharmacology Study Guide Nurseslabs
Pdf Effects Of Surfactants On Preterm Infant Lungs
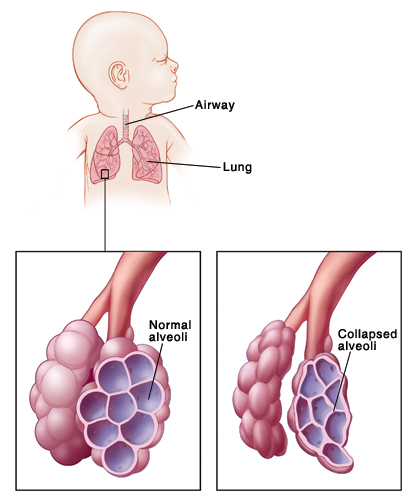
Respiratory Distress Syndrome In The Premature Infant Saint Luke S Health System
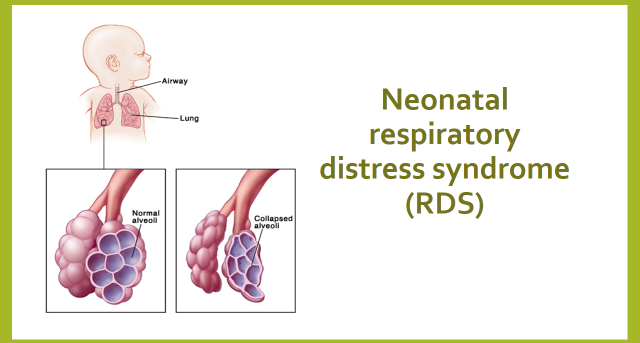
Respiratory Distress In Infants And Adults Brave Beginnings

Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rds Birth Injury Attorneys

Breathing Problems And Premature Babies
What Is Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rds In A Newborn Neopededu

Less Invasive Surfactant Administration A Word Of Caution The Lancet Child Adolescent Health

Respiratory Distress Syndrome Of The Newborn Rt
The Importance Of Technology Transfer Better World

Treatment Of Breathing Problems In Premature Babies

Support Oxygen Of Infants Blindness Parker Waichman Llp

Betamethasone In Pregnancy Prevention Of Hie

Ventilator Review In The Nicu What Does Positive Pressure Volume Targeted And High Frequency Do Empowering Nicu Parents

Ppv Vs Cpap Neonatal Resuscitation Complications Postive Pressure Ventilation For Newborn

Lung Surfactants And Antenatal Corticosteroids Nursing Pharmacology Osmosis
